We have learned how to declare and initialize variables, you probably want to know how to do something with them. Learning the operators of the Java programming language is a good place to start. Operators are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands, and then return a result.
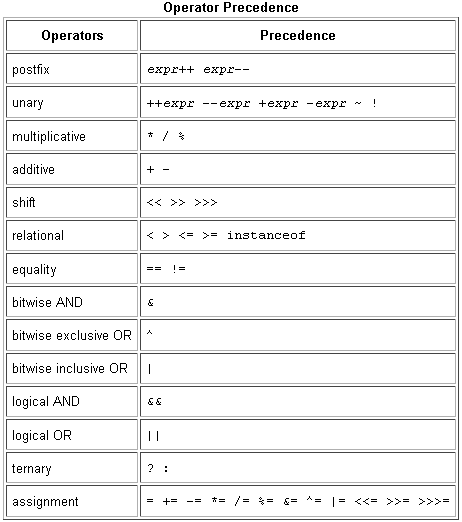
As we explore the operators of the Java programming language, it may be helpful for you to know ahead of time which operators have the highest precedence. The operators in the following table are listed according to precedence order. The closer to the top of the table an operator appears, the higher its precedence. Operators with higher precedence are evaluated before operators with relatively lower precedence. Operators on the same line have equal precedence. When operators of equal precedence appear in the same expression, a rule must govern which is evaluated first. All binary operators except for the assignment operators are evaluated from left to right; assignment operators are evaluated right to left.
Operator Precedence in Java Programming Language
| Operators | Precedence |
|---|---|
| postfix | expr++ expr-- |
| unary | ++expr --expr +expr -expr ~ ! |
| multiplicative | * / % |
| additive | + - |
| shift | << >> >>> |
| relational | < > <= >= instanceof |
| equality | == != |
| bitwise AND | & |
| bitwise exclusive OR | ^ |
| bitwise inclusive OR | | |
| logical AND | && |
| logical OR | || |
| ternary | ? : |
| assignment | = += -= *= /= %= &= ^= |= <<= >>= >>>= |
Assignment Operators in Java Programming Language
One of the most common operator is the simple assignment operator "=".| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Simple assignment operator, Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand | C = A + B will assign value of A + B into C |
| += | Add AND assignment operator, It adds right operand to the left operand and assign the result to left operand | C += A is equivalent to C = C + A |
| -= | Subtract AND assignment operator, It subtracts right operand from the left operand and assign the result to left operand | C -= A is equivalent to C = C - A |
| *= | Multiply AND assignment operator, It multiplies right operand with the left operand and assign the result to left operand | C *= A is equivalent to C = C * A |
| /= | Divide AND assignment operator, It divides left operand with the right operand and assign the result to left operand | C /= A is equivalent to C = C / A |
| %= | Modulus AND assignment operator, It takes modulus using two operands and assign the result to left operand | C %= A is equivalent to C = C % A |
| <<= | Left shift AND assignment operator | C <<= 2 is same as C = C << 2 |
| >>= | Right shift AND assignment operator | C >>= 2 is same as C = C >> 2 |
| &= | Bitwise AND assignment operator | C &= 2 is same as C = C & 2 |
| ^= | bitwise exclusive OR and assignment operator | C ^= 2 is same as C = C ^ 2 |
| |= | bitwise inclusive OR and assignment operator | C |= 2 is same as C = C | 2 |
For example:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 0;
c = a + b;
System.out.println("c = a + b = " + c );
c += a ;
System.out.println("c += a = " + c );
c -= a ;
System.out.println("c -= a = " + c );
c *= a ;
System.out.println("c *= a = " + c );
a = 10;
c = 15;
c /= a ;
System.out.println("c /= a = " + c );
a = 10;
c = 15;
c %= a ;
System.out.println("c %= a = " + c );
c <<= 2 ;
System.out.println("c <<= 2 = " + c );
c >>= 2 ;
System.out.println("c >>= 2 = " + c );
c >>= 2 ;
System.out.println("c >>= a = " + c );
c &= a ;
System.out.println("c &= 2 = " + c );
c ^= a ;
System.out.println("c ^= a = " + c );
c |= a ;
System.out.println("c |= a = " + c );
}
}
Arithmetic Operators in Java Programming Language
The Java programming language provides operators that perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. There's a good chance you'll recognize them by their counterparts in basic mathematics. The only symbol that might look new to you is "%", which divides one operand by another and returns the remainder as its result.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
+ | Additive operator (also used for String concatenation) |
- | Subtraction operator |
* | Multiplication operator |
/ | Division operator |
% | Remainder operator |
The following example, ArithmeticDemo, tests the arithmetic operators.
class ArithmeticDemo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int result = 1 + 2;
// result is now 3
System.out.println("1 + 2 = " + result);
int original_result = result;
result = result - 1;
// result is now 2
System.out.println(original_result + " - 1 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result * 2;
// result is now 4
System.out.println(original_result + " * 2 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result / 2;
// result is now 2
System.out.println(original_result + " / 2 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result + 8;
// result is now 10
System.out.println(original_result + " + 8 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result % 7;
// result is now 3
System.out.println(original_result + " % 7 = " + result);
}
}
Output
1 + 2 = 3
3 - 1 = 2
2 * 2 = 4
4 / 2 = 2
2 + 8 = 10
10 % 7 = 3
You can also combine the arithmetic operators with the simple assignment operator to create compound assignments. For example, x+=1; and x=x+1; both increment the value of x by 1.
The + operator can also be used for concatenating (joining) two strings together, as shown in the following ConcatDemo program:
class ConcatDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
String firstString = "This is";
String secondString = " a concatenated string.";
String thirdString = firstString+secondString;
System.out.println(thirdString);
}
}
By the end of this program, the variable thirdString contains "This is a concatenated string.", which gets printed to standard output.
Unary Operators in Java Programming Language
The unary operators require only one operand; they perform various operations such as incrementing/decrementing a value by one, negating an expression, or inverting the value of a boolean.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
+ | Unary plus operator; indicates positive value (numbers are positive without this, however) |
- | Unary minus operator; negates an expression |
++ | Increment operator; increments a value by 1 |
-- | Decrement operator; decrements a value by 1 |
! | Logical complement operator; inverts the value of a boolean |
The example program, UnaryDemo, tests the unary operators:
class UnaryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = +1;
// result is now 1
System.out.println(result);
result--;
// result is now 0
System.out.println(result);
result++;
// result is now 1
System.out.println(result);
result = -result;
// result is now -1
System.out.println(result);
boolean success = false;
// false
System.out.println(success);
// true
System.out.println(!success);
}
}
The increment/decrement operators can be applied before (prefix) or after (postfix) the operand. The code result++; and ++result; will both end in result being incremented by one. The only difference is that the prefix version (++result) evaluates to the incremented value, whereas the postfix version (result++) evaluates to the original value. If you are just performing a simple increment/decrement, it doesn't really matter which version you choose. But if you use this operator in part of a larger expression, the one that you choose may make a significant difference.
The following example, PrePostDemo, illustrates the prefix and postfix unary increment operator:
class PrePostDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
int i = 3;
i++;
// prints 4
System.out.println(i);
++i;
// prints 5
System.out.println(i);
// prints 6
System.out.println(++i);
// prints 6
System.out.println(i++);
// prints 7
System.out.println(i);
}
}
Equality and Relational Operators in Java Programming Language
The equality and relational operators determine if one operand is greater than, less than, equal to, or not equal to another operand. The majority of these operators will probably look familiar to you as well. Keep in mind that you must use "==", not "=", when testing if two primitive values are equal.
== equal to
!= not equal to
> greater than
>= greater than or equal to
< less than
<= less than or equal to
The following program, ComparisonDemo, tests the comparison operators:
class ComparisonDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
int value1 = 1;
int value2 = 2;
if(value1 == value2)
System.out.println("value1 == value2");
if(value1 != value2)
System.out.println("value1 != value2");
if(value1 > value2)
System.out.println("value1 > value2");
if(value1 < value2)
System.out.println("value1 < value2");
if(value1 <= value2)
System.out.println("value1 <= value2");
}
}
Output:
value1 != value2
value1 < value2
value1 <= value2
The Conditional Operators in Java Programming Language
The && and || operators perform Conditional-AND and Conditional-OR operations on two boolean expressions. These operators exhibit "short-circuiting" behavior, which means that the second operand is evaluated only if needed.
&& Conditional-AND
|| Conditional-OR
The following program, ConditionalDemo1, tests these operators:
class ConditionalDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int value1 = 1;
int value2 = 2;
if((value1 == 1) && (value2 == 2))
System.out.println("value1 is 1 AND value2 is 2");
if((value1 == 1) || (value2 == 1))
System.out.println("value1 is 1 OR value2 is 1");
}
}
Another conditional operator is ?:, which can be thought of as shorthand for an if-then-else statement (discussed in the Control Flow Statements section of this lesson). This operator is also known as the ternary operator because it uses three operands. In the following example, this operator should be read as: "If someCondition is true, assign the value of value1 to result. Otherwise, assign the value of value2 to result."
The following program, ConditionalDemo2, tests the ?: operator:
class ConditionalDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int value1 = 1;
int value2 = 2;
int result;
boolean someCondition = true;
result = someCondition ? value1 : value2;
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Because someCondition is true, this program prints "1" to the screen. Use the ?: operator instead of an if-then-else statement if it makes your code more readable; for example, when the expressions are compact and without side-effects (such as assignments).
The Type Comparison Operator instanceof
The instanceof operator compares an object to a specified type. You can use it to test if an object is an instance of a class, an instance of a subclass, or an instance of a class that implements a particular interface.
The following program, InstanceofDemo, defines a parent class (named Parent), a simple interface (named MyInterface), and a child class (named Child) that inherits from the parent and implements the interface.
class InstanceofDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent obj1 = new Parent();
Parent obj2 = new Child();
System.out.println("obj1 instanceof Parent: "
+ (obj1 instanceof Parent));
System.out.println("obj1 instanceof Child: "
+ (obj1 instanceof Child));
System.out.println("obj1 instanceof MyInterface: "
+ (obj1 instanceof MyInterface));
System.out.println("obj2 instanceof Parent: "
+ (obj2 instanceof Parent));
System.out.println("obj2 instanceof Child: "
+ (obj2 instanceof Child));
System.out.println("obj2 instanceof MyInterface: "
+ (obj2 instanceof MyInterface));
}
}
class Parent {}
class Child extends Parent implements MyInterface {}
interface MyInterface {}
Output:
obj1 instanceof Parent: true
obj1 instanceof Child: false
obj1 instanceof MyInterface: false
obj2 instanceof Parent: true
obj2 instanceof Child: true
obj2 instanceof MyInterface: true
When using the instanceof operator, keep in mind that null is not an instance of anything.
Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators in Java Programming Language
The Java programming language also provides operators that perform bitwise and bit shift operations on integral types. The operators discussed in this section are less commonly used. Therefore, their coverage is brief; the intent is to simply make you aware that these operators exist.
The unary bitwise complement operator "~" inverts a bit pattern; it can be applied to any of the integral types, making every "0" a "1" and every "1" a "0". For example, a byte contains 8 bits; applying this operator to a value whose bit pattern is "00000000" would change its pattern to "11111111".
The signed left shift operator "<<" shifts a bit pattern to the left, and the signed right shift operator ">>" shifts a bit pattern to the right. The bit pattern is given by the left-hand operand, and the number of positions to shift by the right-hand operand. The unsigned right shift operator ">>>" shifts a zero into the leftmost position, while the leftmost position after ">>" depends on sign extension.
The bitwise & operator performs a bitwise AND operation.
The bitwise ^ operator performs a bitwise exclusive OR operation.
The bitwise | operator performs a bitwise inclusive OR operation.
The following program, BitDemo, uses the bitwise AND operator to print the number "2" to standard output.
class BitDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int bitmask = 0x000F;
int val = 0x2222;
// prints "2"
System.out.println(val & bitmask);
}
}
Overview of Operators in Java Programming Language
The following quick reference summarizes the operators supported by the Java programming language.
Simple Assignment Operator
= Simple assignment operator
Arithmetic Operators
+ Additive operator (also used
for String concatenation)
- Subtraction operator
* Multiplication operator
/ Division operator
% Remainder operator
Unary Operators
+ Unary plus operator; indicates
positive value (numbers are
positive without this, however)
- Unary minus operator; negates
an expression
++ Increment operator; increments
a value by 1
-- Decrement operator; decrements
a value by 1
! Logical complement operator;
inverts the value of a boolean
Equality and Relational Operators
== Equal to
!= Not equal to
> Greater than
>= Greater than or equal to
< Less than
<= Less than or equal to
Conditional Operators
&& Conditional-AND
|| Conditional-OR
?: Ternary (shorthand for
if-then-else statement)
Type Comparison Operator
instanceof Compares an object to
a specified type
Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators
~ Unary bitwise complement
<< Signed left shift
>> Signed right shift
>>> Unsigned right shift
& Bitwise AND
^ Bitwise exclusive OR
| Bitwise inclusive OR
Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables.